
To select the right racking system for your warehouse, evaluate your available space, inventory requirements, and operational objectives. Focus on enhanced efficiency, safety, and future adaptability. You should consider product types, turnover rates, and compatibility with existing equipment. Common operational goals include:
A thoughtful approach helps you optimize your distribution centre and supports long-term growth.
Measure your warehouse space carefully, including floor area and clear height, to choose racks that fit safely and maximize storage.
Analyze your inventory types and turnover rates to pick racking systems that improve access and storage efficiency.
Match your racking choice to your equipment and workflow needs, keeping aisles wide enough for safe and smooth movement.
Consider load capacity and safety rules to protect staff and goods; inspect racks regularly and train your team well.
Plan your budget wisely by balancing cost with quality and scalability to support future growth and reduce long-term expenses.

Accurate measurement of your warehouse is the foundation for selecting an optimal racking system. Begin by determining the total floor area and clear vertical height. Standard upright frame heights range from 8 to 40 feet, with depths between 24 and 48 inches. You should measure the clear height, which is the distance from the floor to the lowest overhead obstruction. This measurement dictates how you maximize vertical space and comply with fire safety codes, such as maintaining at least 18 inches below sprinkler heads. Calculate frame depth by subtracting six inches from the pallet depth, ensuring proper beam support. Always allow a minimum clearance of 4 inches between the top of the loaded pallet and the beam above for safe handling. High rack heights may require special permits and adherence to local safety regulations. These steps help you achieve space efficiency and support future expansion.
Inventory analysis plays a critical role in racking system selection. You must evaluate inventory types, turnover rates, and SKU density. Employ methods such as Just-in-Time inventory systems and inventory management software to track stock levels and automate replenishment. Calculate inventory turnover ratios using average inventory to smooth fluctuations. Adjust inventory levels based on seasonal demand and use forecasting tools to predict future needs. High SKU density favors selective racking systems for easy accessibility, while low SKU density with high volume per SKU supports high-density options like drive-in racks. Regular inventory analysis ensures you avoid overstocking or understocking, optimizing warehouse logistics and supporting distribution centre operations.
Use inventory management software for real-time tracking.
Separate long-term and short-term storage based on turnover rates.
Review inventory data regularly to maintain accuracy.
Assessing equipment movement and accessibility is essential for efficient warehouse operations. Focus on material flow and the types of handling equipment, such as forklifts, reach trucks, and turret trucks. Evaluate aisle widths, turning radius, and dock positioning to prevent bottlenecks. Maintain proper aisle widths, typically 12 feet for standard forklifts, to ensure easy accessibility. Integrate safety features like guardrails and marked pedestrian walkways to separate equipment zones. Conduct regular inspections and train staff on safety protocols. Utilize warehouse management systems to map and monitor racking layouts, optimizing equipment movement and supporting space efficiency.
Choose racking configurations based on equipment type and operational needs.
Implement digital tools for layout optimization.
Schedule routine maintenance to identify hazards and inefficiencies.

Choosing the right warehouse racking systems ensures you maximize space, improve workflow, and support your operational goals. The following table summarizes the main types of warehouse shelves, their descriptions, and typical use cases:
| Racking Type | Description | Typical Use Cases |
| Selective Pallet Racks | Direct access to every pallet, single-deep configuration | Varied SKUs, high turnover warehouses |
| Drive-In/Drive-Through Racks | Forklifts enter lanes for high-density storage | Bulk storage, cold storage, raw materials |
| Push-Back Racks | Pallets stored 2-6 deep, loaded from one aisle | Bulk retail, moderate turnover |
| Pallet Flow Racks | Gravity rollers for FIFO rotation | Distribution, food, fast-moving goods |
| Cantilever & Specialty Racks | Store long, bulky, or irregular items | Lumber, pipes, furniture, specialty goods |
| Mobile & Automated Systems | Racks move on tracks or use automation | High-density, scalable, tech-driven ops |
You will find selective pallet racks as the most common warehouse shelves. This racking system gives you direct access to every pallet, making it ideal for warehouses with many SKUs and frequent inventory changes. You can adjust beam heights to fit different product sizes. Selective racks support FIFO and FEFO inventory methods. They work well with standard forklifts and allow you to reconfigure layouts as your needs change. However, they require wider aisles, which can limit enhanced storage capacity compared to high-density racking systems.
Drive-in and Drive-through racking systems help you achieve high-density storage by eliminating most aisles. Forklifts drive directly into the rack lanes, storing pallets several positions deep. Drive-in racks use a LIFO approach, making them perfect for storing large quantities of similar products with low turnover. Drive-through racking supports FIFO, allowing you to load from one side and unload from the other. These warehouse shelves are popular in cold storage, wholesale, and manufacturing. You can increase storage density by up to 75% with these systems, making them a top choice for high-density racking systems.
Pallet flow racks use gravity rollers to move pallets from the loading end to the picking end, supporting FIFO inventory rotation. This system works best for date-sensitive or perishable goods. Push-back racks store pallets on nested carts, allowing you to load and retrieve from the same aisle. Push-back racks operate on a LIFO basis and suit moderate turnover SKUs. Both systems reduce the number of aisles needed, improving space efficiency and warehouse workflow. You can combine these warehouse shelves to match different product turnover rates.
Cantilever Racks provide flexible storage for long, heavy, or awkward items such as lumber, pipes, and furniture panels. You can use specialty racks like reel racks for cables, roll-out racks for easy access, and stack racks for non-standard loads. These warehouse shelves adapt to unique materials and industry-specific requirements, giving you more options for organizing your space.
Motorized Mobile Pallet Racking System mount warehouse shelves on tracks, letting you move entire rows to open access aisles only when needed. Automated systems, such as shuttle racking, AS/RS stacker cranes, and radio shuttles, use advanced technology to handle pallets and boxes. You can increase storage density by up to 80% and reduce labor costs with these solutions. High Bay and Clad-rack systems maximize vertical space, while VNA racking narrows aisles for more pallet positions. Mezzanine racks add extra storage levels within your existing warehouse. Mobile shelving works well for small items or documents. These warehouse racking systems offer scalable, efficient, and customizable solutions for modern operations.
Selecting the right racking system for your warehouse requires a careful match between system specifications and your operational needs. You must consider several criteria to ensure the solution supports your workflow, safety, and future growth.
Load capacity stands as a critical factor in racking system selection. Begin by identifying the type of racking you need, such as selective, drive-in, or cantilever. Measure rack dimensions—height, width, and depth—to understand how weight distributes across beams and uprights. Always check manufacturer specifications for maximum load capacities and apply a safety margin by reducing the stated maximum load. For example, if a beam supports 2,000 lbs, limit your load to 1,800 lbs for added safety.
Safety standards differ by region and industry. The table below highlights key differences between the USA and Canada:
| Aspect | SA | Canada |
| Regulatory Standards | ANSI MH16.1, OSHA inspections | CSA A344, OHSA |
| Rack Dimensions | Depth: 36-48 in, Height: 96-120 in | Depth: 900-1200 mm, Height: 2400-3000 mm |
| Aisle Width | Min. 30 in (single), 48 in (double) | Min. 1.2 m (single), 1.5 m (double) |
| Seismic Requirements | Stricter in earthquake zones | Varies by province |
| Inspection Frequency | Every 6 months | Regular, no specific frequency |
| Certification & Training | Not mandatory, recommended | Required for installers/operators |
You must comply with local regulations, including proper installation, clear load labeling, and regular staff training. Use technology such as load sensors to detect overloads early. Maintain thorough documentation of inspections and maintenance to support a strong safety culture.
Budget planning plays a central role in your racking system decision. Costs vary widely based on system type, warehouse size, and installation complexity. The chart below compares average costs per pallet position for common racking systems:
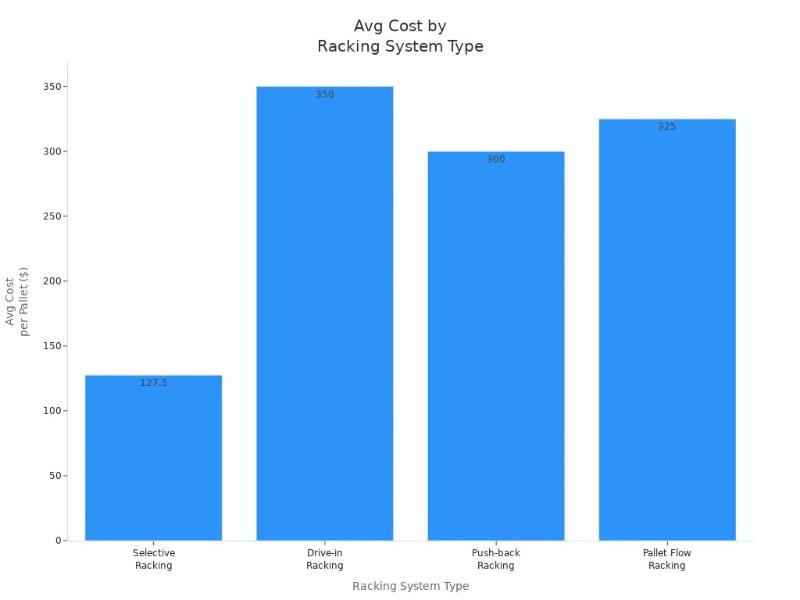
| Racking System Type | Cost Range per Pallet Position | Notes on Installation and Additional Costs |
| Selective Racking | $55 - $200 | Basic system, lower cost per position |
| Drive-in Racking | $200 - $500 | Higher density, more complex installation |
| Push-back Racking | $200 - $400 | Better space utilization, higher price |
| Pallet Flow Racking | $200 - $450 | High throughput, saves labor and space |
Installation labor typically adds 15-35% to equipment costs. Permits, engineering, and seismic compliance can add another 10-30%. Accessories and safety features may increase costs by 35-65%. Steel price volatility can impact final pricing, so timing your purchase is important. Used racking can save 20-40% but may require more maintenance.
When working within budget constraints, focus on the best solution cost rather than the lowest price. Investing in high-quality, modular, and scalable systems reduces repair costs and supports future expansion. Obtain multiple supplier quotes and prepare detailed specifications to secure competitive pricing. Bulk purchasing and hybrid solutions, such as combining new uprights with used beams, can further reduce costs.
Scalability ensures your racking system adapts as your business grows. Choose modular solutions that allow you to adjust, expand, or reconfigure storage as inventory needs change. Mobile racking systems can nearly double storage capacity by maximizing unused aisle space. Durable materials and flexible designs help you balance cost and lifespan.
Follow these best practices for scalability:
Plan for expansion by mapping your warehouse layout, including fixed elements like columns and doors.
Maximize vertical space while maintaining accessibility for equipment and staff.
Integrate technology infrastructure to support future automation.
Select storage systems that match current needs but remain flexible for future changes.
Compliance with safety and regulatory standards protects your staff and assets. In the United States, follow OSHA, ANSI, and Rack Manufacturers Institute (RMI) guidelines. Ensure racks have clear load labels, maintain safe aisle spacing, and conduct regular inspections. Train staff on hazard identification and proper use of personal protective equipment. Use quality materials and protective devices such as rack guards to prevent accidents.
A well-planned racking system selection process considers load capacity, safety, budget, scalability, and compliance. This approach ensures your warehouse remains efficient, safe, and ready for future growth.
Copyright @ 2026 Nanjing Huayide Logistics Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
 network supported
network supported
Sitemap / Xml / Blog / Privacy Policy